Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is the condition where skin cell is at the wrong place. In normal condition, external ear canal is covered by squamous cell epithelium. This epithelium is not available in the middle ear and bone. Cholesteatoma occur when this some of this squamous epithelium have been displaced or appeared in the middle ear, skull base or mastoid. The epithelium will produce the keratin and the desquamation will contribute to cholesteatoma formation.
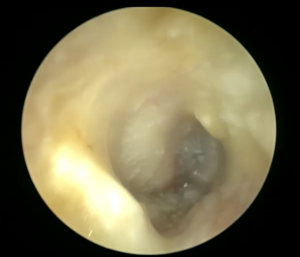
Chronic Ear Discharge could be easily mistaken as chronic ear infection if no proper ear toilet is done to clear off all the debris.
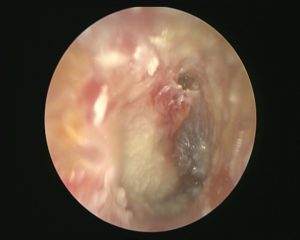
Post Ear Toileting and cleaning of the whitish debris noted a perforation at the upper part of the ear drum. Medial to the ear drum noted to have a whitish mass. Proper diagnosis cholesteatoma
Accumulation of the cholestateatoma which consist of granulation tissue, keratin debris, enzyme and inflammatory markers will cause local erosion to the surrounding structures. In the middle ear, erosion of small bones of the ear will cause hearing loss, meanwhile erosion of the vestibular organ will cause vertigo or dizziness in the patient. Erosion of the facial nerve canal will cause weakness of the facial muscle and erosion to the brain will cause blood clot formation and also brain infection. Its is a locally aggressive slow growing disease which if left untreated might give rise to severe complications.
Mastoidectomy could be done to to eradicate the disease. It is a very fine operation which require operating microscope and also high speed drill. The disease might persist or recur if the air cell in hidden areas are not probably opened up.